DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2024.3376823
Abstract
The conventional piezoelectric-hydraulic hybrid actuator consists of a hydraulic pump driven by a piezoelectric stack along with a hydraulic cylinder and is envisioned as a potential actuator for a trailing edge flap on a full-scale smart rotor system. For this type of actuator, the inertial force caused by the flow pulsation of the liquid will significantly degrade its output performance. To solve these issues, two thin plates connected with counterweights are embedded in the hybrid actuator to act as two mechanical band-stop filters, and its working principle is illustrated by the mechanic-electric-hydraulic analogy. Its configuration is presented in detail, and the output performance is tested. The experimental results show that when the excitation frequency is close to the resonance frequency of the mechanical filter in the hydraulic system, the pulsation rate is reduced, the influence of the inertial force on the actuator is weakened, and its output performance is relatively significantly enhanced. The maximum velocity of the new hybrid actuator with a blocking force of 125 N has been increased from 27.3 mm/s to 48 mm/s. This strategy has proven effective for piezoelectric-hydraulic hybrid actuators and can be adopted by many other electrohydraulic actuators for performance improvement.
文章摘要
传统的压电-液压混合作动器由压电堆驱动的液压泵和液压缸组成,有望作为全尺寸智能转子系统后缘襟翼的作动器。对于该类作动器,液体脉动引起的惯性力将显著降低其输出性能。针对该问题,在混合作动器中嵌入两块与配重块连接的薄板作为两个机械带阻滤波器,并通过机电液类比说明其工作原理。本文详细介绍了其结构,并测试了其输出性能。实验结果表明,当激励频率接近液压系统中机械滤波器的共振频率时,脉动率显著降低,惯性力对作动器的影响明显减弱,混合作动器输出性能得到了相对明显的提高。新型混合作动器在阻塞力为125 N时的最大速度由27.3 mm/s提高到48 mm/s。该策略已被证明对压电-液压混合作动器有效,并可被许多其他电液作动器采用以提高性能。
图片摘要
(a) (b)
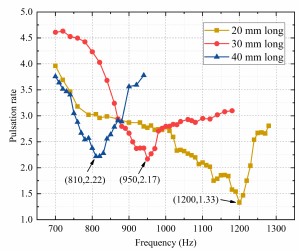
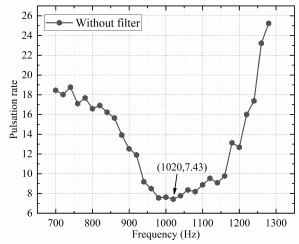
图一:脉动率对混合作动器激励频率的依赖性:(a)对于新型混合作动器,(b)对于传统的混合作动器
在采用机械滤波器的3种情况下,这些新型混合作动器的脉动率变化趋势相似。总体而言,随着频率的增加,脉动率逐渐减小至最低值,随后又增加。这是意料之中的,因为当激励频率f接近液压系统中机械滤波器的谐振频率fr时,脉动抑制会得到增强,当这两个频率相等时,抑制效果最好。这几种新型混合作动器在配重长度为20 mm、30 mm和40 mm时,最小脉动率分别为1.33、2.17和2.22,分别在1 200 Hz、950 Hz和810 Hz下获得。此外,这些新型混合作动器的最佳工作频率略低于固体力学中模拟的这些机械滤波器的共振频率(分别为1270 Hz、990 Hz和840 Hz)。这是因为薄板的振动会引起周围流体对其施加的振荡的流体力,从而增加附加质量和结构阻尼,最终降低其共振频率。对于传统混合作动器,在1020 Hz之前,脉动率随频率的增加而减小,在1020 Hz时脉动率达到最小值7.43;随着频率的继续增加,脉动率不断增大,这是由液压回路和油管的动态特性引起的。在测试的频率范围内,新型混合作动器的脉动率低于传统混合作动器,验证了该策略的有效性。
亮点
本文提出了一种应用于压电-液压混合作动器系统的机械带阻滤波器,该滤波器由薄板以及配重块组成。设计的薄板和配重块结构简单,易于装配。实验结果证实:该策略成功平滑了液体的脉动,有利于降低惯性力对压电堆的影响,提高压电堆的性能。此外,该策略为其他电液执行器提高输出性能奠定了良好的基础。